Bone Expansion
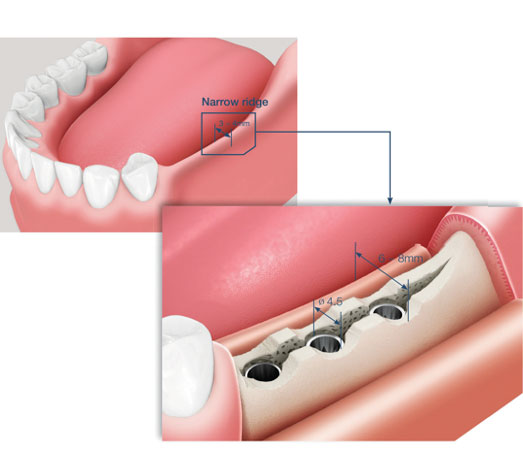
Bone expansion, also known as osteotome sinus floor elevation or bone spreading, is a dental surgical technique used to increase the bone volume in the posterior maxilla (upper jaw) to enable the placement of dental implants. The procedure is typically performed when there is inadequate bone height in the upper jaw due to the enlargement of the maxillary sinus or other bone loss factors.
The process of bone expansion involves the following steps:
1. Preoperative Assessment: The dentist or oral surgeon performs a thorough examination, including dental imaging (such as X-rays or CT scans), to assess the amount of available bone and the dimensions of the maxillary sinus.
2. Anesthesia: The patient is given local anesthesia to numb the area where the bone expansion will take place, ensuring a comfortable procedure.
3. Osteotomy: A small incision is made in the gum tissue to access the underlying bone. Then, a series of specially designed instruments called osteotomes are used to create a controlled fracture in the bone.
4. Bone Expansion: The osteotomes are carefully tapped or gently hammered into the bone, causing it to expand and move upward. This process lifts the sinus membrane upward, effectively creating additional space beneath it.
5. Bone Grafting (optional): In some cases, bone graft materials may be added to the newly created space to enhance bone regeneration and support dental implant stability.
6. Dental Implant Placement: After the bone expansion and any necessary bone grafting, dental implants can be inserted into the newly created bone space. Dental implants are artificial tooth roots that serve as anchors for dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, or dentures.
7. Suture and Healing: The gum tissue is sutured back in place, and the area is allowed to heal. Over time, the bone around the dental implants fuses with the surrounding bone in a process called osseointegration.
Bone expansion is a less invasive alternative to traditional sinus lift procedures, which require access to the sinus cavity through a window in the lateral wall of the maxilla. It is often preferred for cases with minimal bone height, avoiding the need for more complex surgical interventions.
As with any dental or surgical procedure, bone expansion has potential risks and complications, so it’s crucial for patients to consult with a qualified dental professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on their specific needs and oral health conditions.
Recent Posts